How to reuse GIN datasets
Our datasets are managed with datalad. Datalad allows the versioning and distribution of large datasets. Datalad relies on another tool called git-annex, which itself is an extension of git providing support for large file versioning with a high flexibility.
We host the data on GIN. GIN’s interface is really similar to GitHub, but unlike the latter, GIN can handle our large files.
Installing datalad
The DataLad handbook provides extensive instructions for the installation of DataLad in their handbook.
If you have admin rights and you are working on Linux or Mac, the following should work:
Install git-annex using
apt install git-annex(linux) orbrew install git-annex(mac). Git-annex is available by default on Oberon.Install datalad with pip :
pip3 install datalad
Note
If you are having permission issues, consider using python virtual environments or conda (see DataLad’s handbook). Otherwise, refer to your system administrator.
Setup your GIN account
Most repositories are private, and thus require authentication. We recommend that you always use SSH authentication and we will only provide instructions for this case.
Before anything, you will need to create an account on GIN, and to link your SSH public key to your GIN account.
Create an account on GIN
Copy your SSH public key (usually located in
~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub)Click on the blue button ‘Add a key’ and paste your public key where requested.
Note
Remember to communicate your username to the data administrator before you try to access the data in order for him to grant you permissions.
Note
You can configure as many keys as necessary. This is useful when you need to access GIN from different locations with different SSH keys (e.g. from your lab cluster, or from your own laptop).
Note
You may consider enabling the Keychain
(append ~/.ssh/config with UseKeychain yes)
if you are prompted for your SSH passphrase everytime.
Installing a dataset
Installing a dataset can be done with the datalad install command. The input is the SSH location of the dataset. It can be found on the page of the repository on GIN:
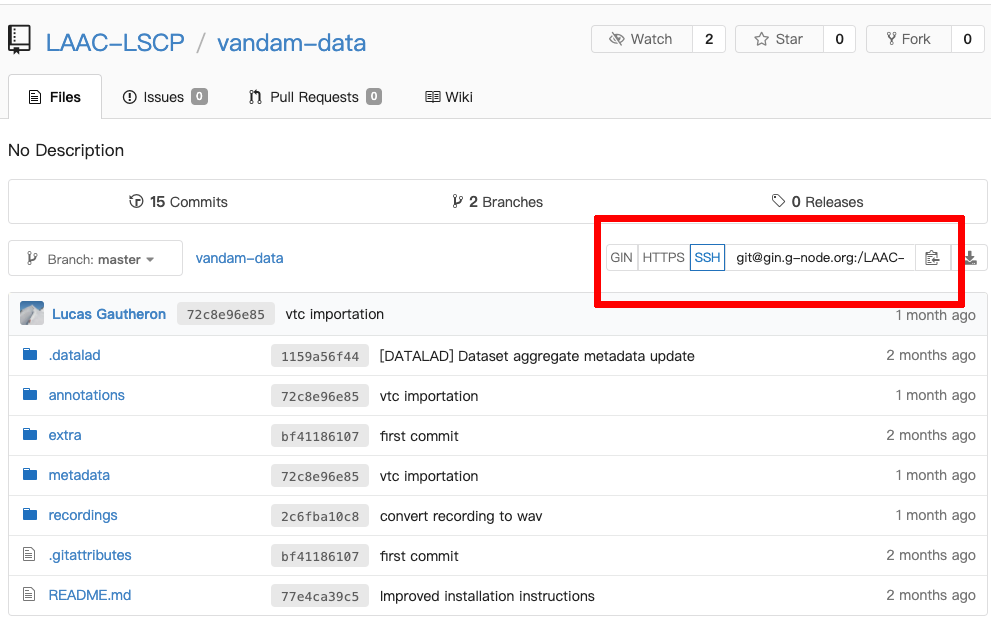
A GIN dataset.
For instance, the VanDam public dataset (available on GIN) can be installed with the following command:
datalad install git@gin.g-node.org:/LAAC-LSCP/vandam-data.git
cd vandam-data
Datasets that contain subdatasets can be installed recursively using the -r switch. This is the case of the EL1000 dataset:
datalad install git@gin.g-node.org:/EL1000/EL1000.git
cd EL1000
Warning
Some datasets may require additional configuration steps. Pay attention to the README before you start using a dataset.
That’s it ! Your dataset is ready to go. By default, large files do not get downloaded automatically. See the next section for help with downloading those files.
Downloading large files
Files can be retrieved using datalad get [path]. For instance,
datalad get recordings will download all recordings.
Note
Technically speaking, the large files in your repository are symbolic links pointing to their actual location, somewhere under .git. You can ignore that and read/copy the content of these files as if they where actual files.
Warning
If you want to edit the content of a large file, you will need to unlock it
beforehand, using datalad unlock,
e.g.: datalad unlock annotations/vtc/converted.
Updating a dataset
A dataset can be updated from the sources using git pull together
with datalad update.
Contributing
Pushing changes to a dataset
You can save local changes to a dataset with
datalad save [path] -m "commit message". For instance :
datalad save annotations/vtc/raw -m "adding vtc rttms"
datalad save is analoguous to a combination of git add and
git commit.
These changes still have to be pushed, which can be done with :
datalad push